Wargamay (Pama-Nyungan)
Wargamay is described by Dixon (1981). Dixon is the only source on Wargamay, and he does not posit complex segments for the language. But he does mention a few suggestive facts:
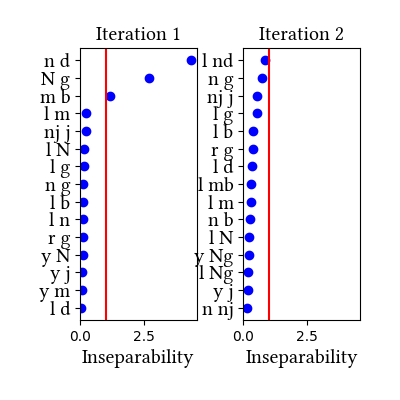
The learner's outcome in this case is similar to Sundanese: it identifies homorganic nasal-stop clusters as complex segments. From the point of view of distribution, NC clusters are inseparable. Thus, just as in Sundanese, this could be a learning-theoretic argument for a complex segment analysis.
Dixon, Robert M. W. 1981. Wargamay. In Handbook of Australian Languages, ed. Robert M. W. Dixon and B. J. Blake, volume 2. Amsterdam: John Benjamins.
The data source is Hayes and Wilson's (2008) lexicon for Wargamay, available on Bruce's site.
Simulation data at a glance
Click on simulation name to view additional simulation details.
| Simulation name | Initial state Learning Data | Initial state features |
|---|---|---|
| only version | LearningData.txt | Features.txt |
Simulation details for Wargamay
| Iteration | Learning Data produced | Features produced | Inseparability | New Segments added | Segments removed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | LearningData.txt | Features.txt | [download] [view] | Ng, mb, nd | None |
| 2 | No new learning data | No new features | [download] [view] | None | None |