Bolivian/Peru Quechua (Quechuan)
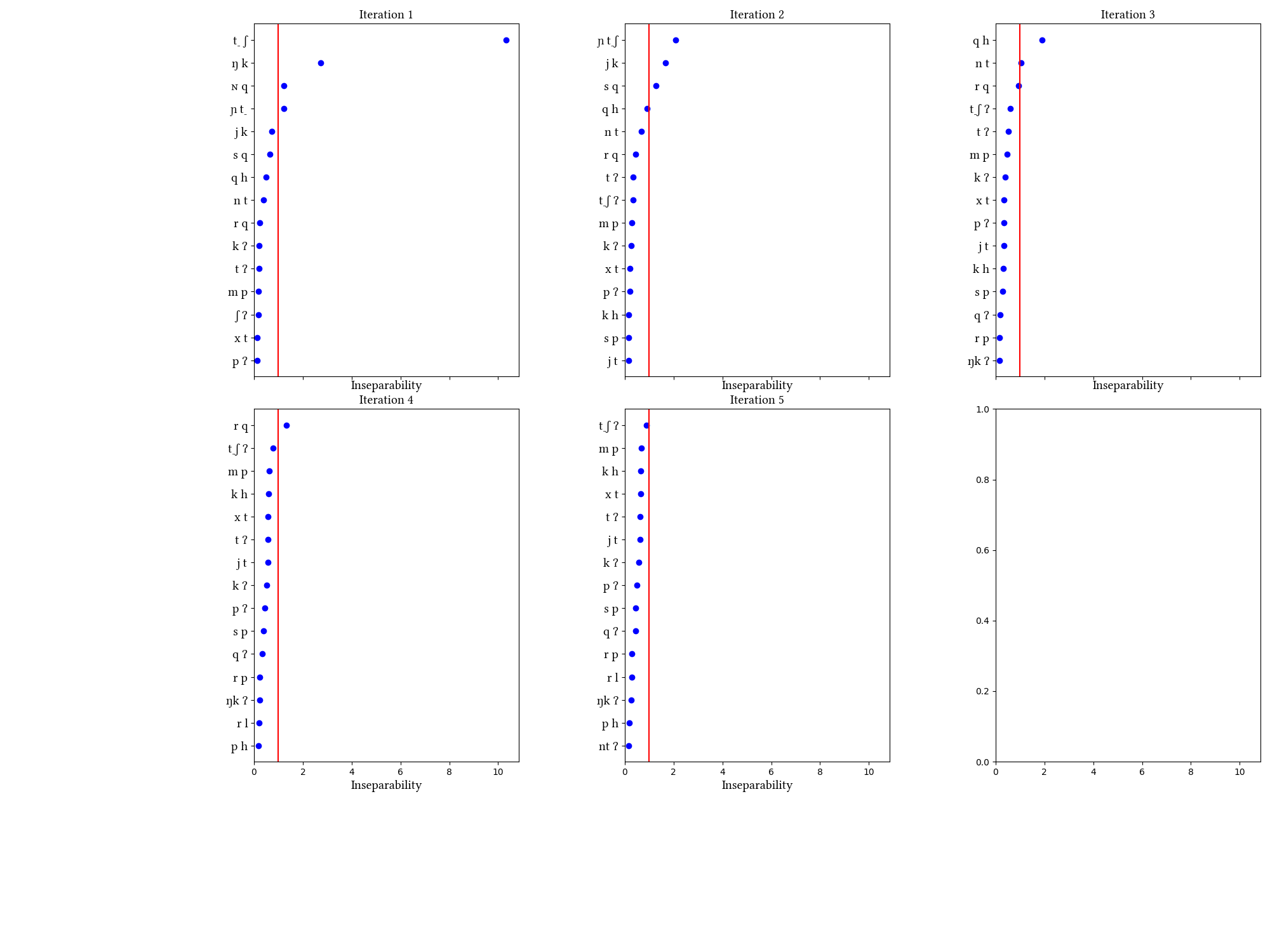
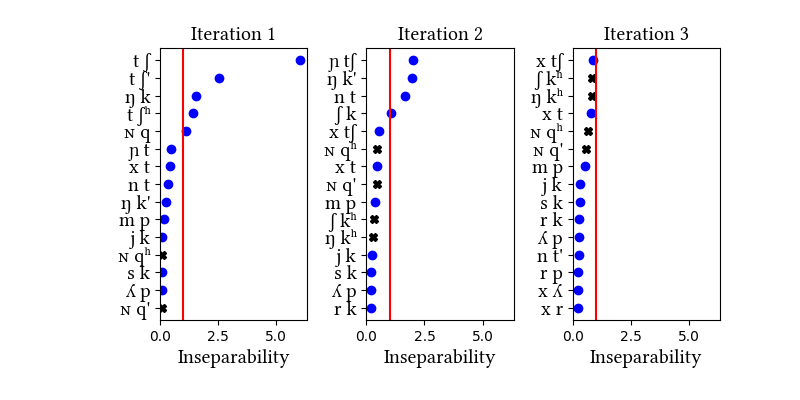
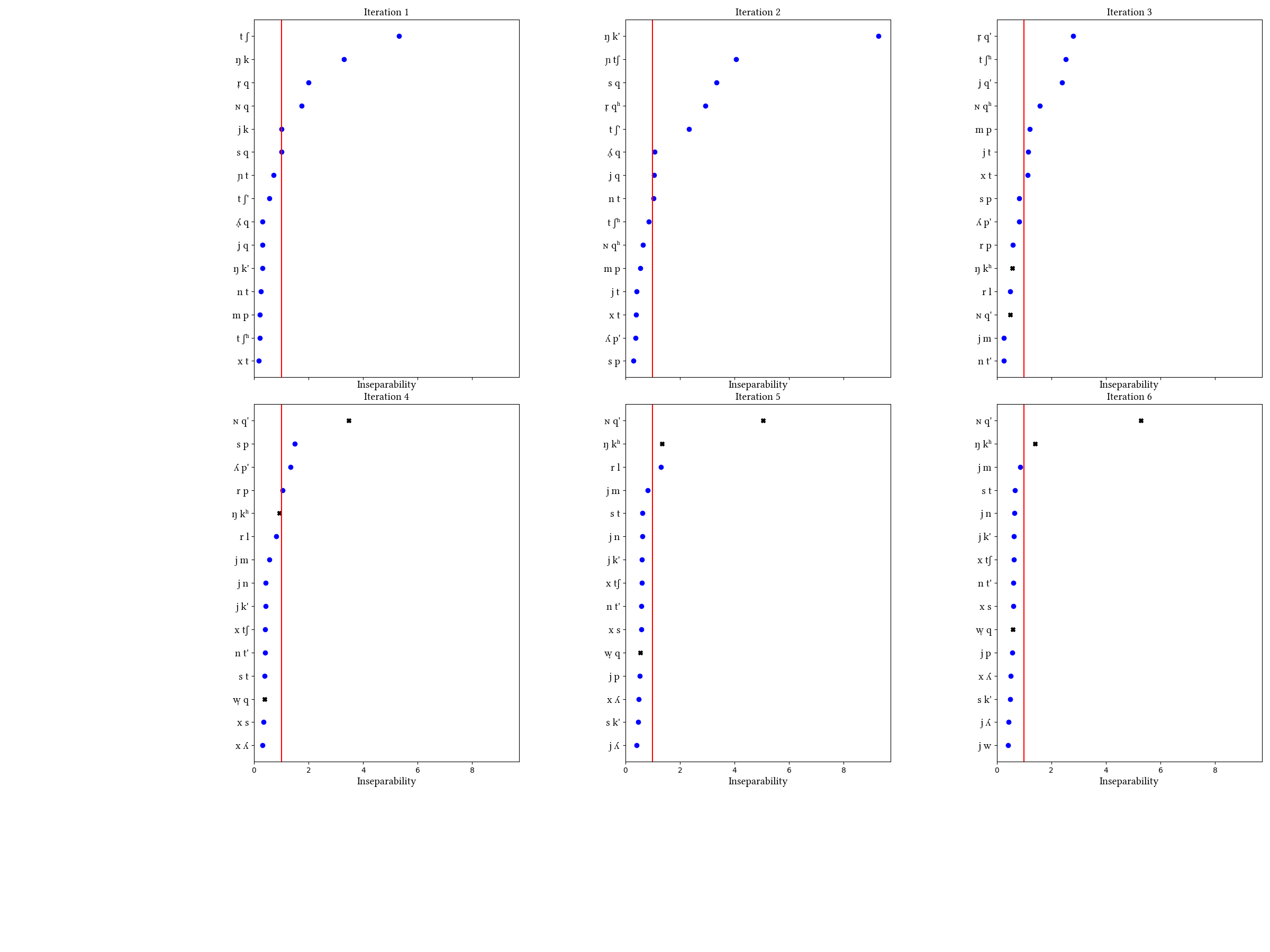
Quechua is the discussed in the paper, and the one that most clearly highlights the problem of the nature of the learning data. As described in the paper, the simulations on word corpora fail in various ways to arrive at the posited (uncontroversial) inventory of affricates. The reason is that the phonotactics and morphology of Quechua conspire to inflate the frequencies of certain clusters, diluting the frequencies of affricates. Reasonable-looking results arrive only when the learner is trained on more abstract data: roots or a morpheme list. Quechua is also a case where we tried to decompose aspirated and ejective plosives into more primitive parts. The learner does not find these segments when trained on words.
In addition to various kinds of "one-word-per-line" datasets, we trained the learner on a corpus of connected, child-directed speech. This is for a different dialect, Peruvian Quechua, but it is sufficiently close to Bolivian Quechua to draw some conclusions. The learner does not over-unify insane clusters in this simulation, but it also does not find the aspirated affricate--its inseparability value trails clusters that are frequent in common affixes, so the learner is unlikely to find it in such data.
Simulation data at a glance
Click on simulation name to view additional simulation details.
Simulation details for Quechua words_with_mb
Input:
Summary of iterations:
| Iteration | Learning Data produced | Features produced | Inseparability | New Segments added | Segments removed |
|---|
| 1 |
LearningData.txt |
Features.txt |
[download] [view] |
tʃ, sq, jk, ŋk, ɴq |
None |
| 2 |
LearningData.txt |
Features.txt |
[download] [view] |
tʃ', tʃʰ, nt, ɲtʃ, rq, ʎp', ŋk' |
ʃ', ʃʰ |
| 3 |
LearningData.txt |
Features.txt |
[download] [view] |
sp, xt, rp, rl, ɴqʰ |
None |
| 4 |
LearningData.txt |
Features.txt |
[download] [view] |
sk', xs, mp, nt', rqʰ, ʎq, jk' |
None |
| 5 |
LearningData.txt |
Features.txt |
[download] [view] |
sk, sq', xʎ, jt, jw |
None |
| 6 |
LearningData.txt |
Features.txt |
[download] [view] |
ʃk, mp', rk', rm, lt, ʎp, jʎ, wp, ws |
None |
| 7 |
LearningData.txt |
Features.txt |
[download] [view] |
st', ʃkʰ, xr, xtʃ, ɲtʃ', ʎtʃ', jq, jn |
None |
| 8 |
LearningData.txt |
Features.txt |
[download] [view] |
xt', xtʃ', rk, rq', lw, jm, jtʃ' |
None |
| 9 |
LearningData.txt |
Features.txt |
[download] [view] |
sp', xj, mpʰ, rkʰ, lm, jq', jr |
None |
| 10 |
LearningData.txt |
Features.txt |
[download] [view] |
ʃw, xp, xw, rw, js |
None |
| 11 |
LearningData.txt |
Features.txt |
[download] [view] |
nr, rt, ʎm |
None |
| 12 |
LearningData.txt |
Features.txt |
[download] [view] |
st, xn, ms, ʎk, jtʃ |
None |
| 13 |
LearningData.txt |
Features.txt |
[download] [view] |
sm, xm |
None |
| 14 |
LearningData.txt |
Features.txt |
[download] [view] |
ns |
None |
| 15 |
No new learning data |
No new features |
[download] [view] |
None |
None |
Summary of inventory changes
| Stage | Consonant set |
|---|
| Input | p t k q p' t' ʃ' k' q' pʰ tʰ ʃʰ kʰ qʰ s ʃ x h m n ɲ r l ʎ j w ŋ ɴ r̞ l̞ ʎ̞ j̠̠ w̞ |
| Output | p t k q p' t' k' q' pʰ tʰ kʰ qʰ s ʃ x h m n ɲ r l ʎ j w ŋ ɴ l̞ w̞ tʃ jk ŋk ɴq r̞q tʃ' sq nt ɲtʃ ŋk' r̞qʰ ʎ̞q j̠̠q tʃʰ xt mp jt ɴqʰ r̞q' j̠̠q' sp rp ʎp' rl |
Simulation Plots
Simulation details for Quechua words glot_feats_as_segs
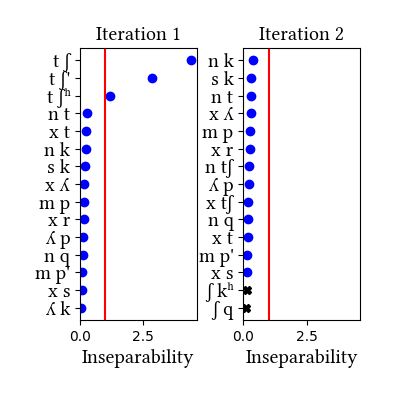
This simulation demonstrates that not only does it not help to break down aspirated and ejective plosives into sequences in this case--it actually makes things worse. Certain laryngeally marked stops [kʰ, t'] are so infrequent that they fail to be unified, whereas clusters common in morphologically complex words do get unified.
Input:
This version of the Quechua word list transcribes ejectives and aspirates as sequences with glottal stops and [h] respectively.
Summary of iterations:
Summary of inventory changes
| Stage | Consonant set |
|---|
| Input | p t k q p' t' ʃ' k' q' pʰ tʰ ʃʰ kʰ qʰ s ʃ x h m n ɲ r l ʎ j w ŋ ɴ |
| Output | p t k q p' t' k' q' pʰ tʰ kʰ qʰ s ʃ x h m n ɲ r l ʎ j w tʃ tʃ' sq ɲtʃ jk nk tʃʰ nt rq nq xt mp jt sp ʎp' rp rl |
Simulation Plots
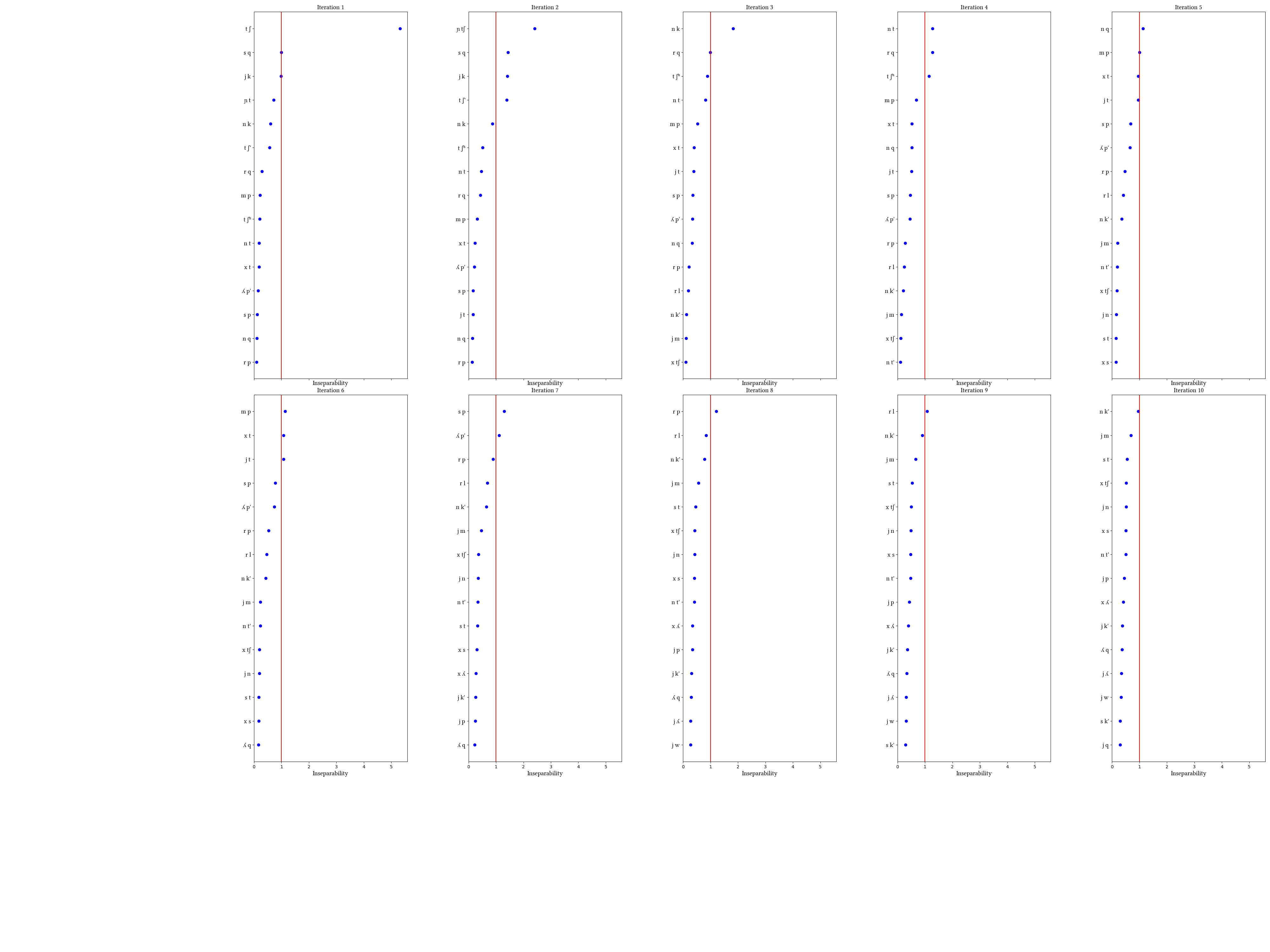

Simulation details for Quechua childes_cds
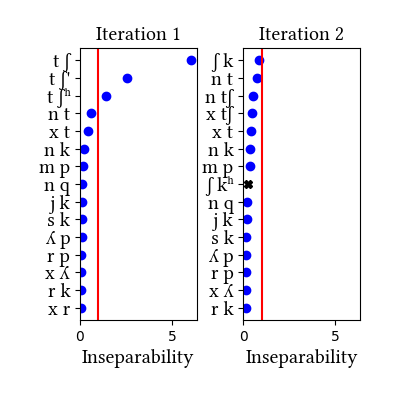
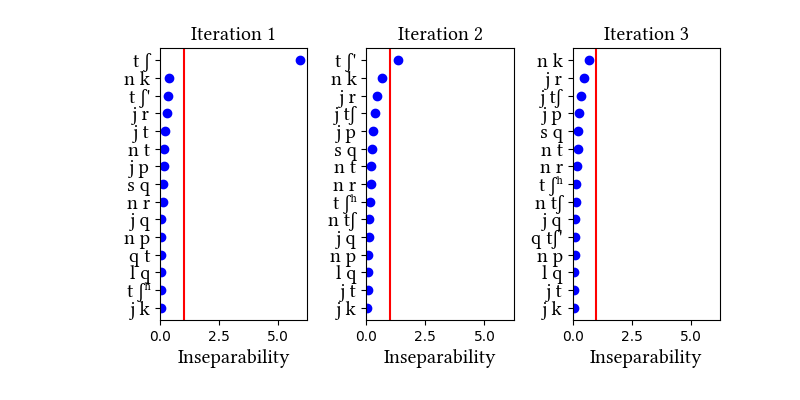
This simulation comes close to finding the target inventory [tʃ, tʃ', tʃʰ]--the learner finds the plain and ejective affricates, but not the aspirated one. It is clear from the inseparability measures that this dataset raises the same issues as the morphologically complex word corpus; once the two affricates are unified, the runner-up clusters are those that are frequent in common suffixes, and [tʃʰ] is not a candidate for unification. It trails [s q], [j p], [j tʃ], [n t], and others. So, unless this particular example of child-directed speech is atypical of Quechua, it really looks as though roots and morphemes are the right source of distributions for finding affricates.
Input:
This corpus is 10633 utterances from the CHILDES database for Peruvian Quechua experiments described in Gelman et al. 2015. We took all the utterances produced by mothers in the experiments, transcribed them from orthography, and removed punctuation and spaces between words.
Note that there are differences between this dialect and the one described in our paper. This one appears to allow stops in coda position, and the data also have not been cleaned of various loanword segments such as /b, d, g, f/. The dataset is also thematically limited, since the mothers and children were discussing picture books. The overall size of the dataset is not large, although it represents 47 different conversations (46 distinct speakers).
Gelman, Susan A., Bruce Mannheim, Carmen Escalante, and Ingrid Sanchez Tapia. "Teleological talk in parent–child conversations in Quechua." First Language 35, no. 4-5 (2015): 359-376.
Summary of iterations: