Classical / Vulgar Latin (Indo-European)
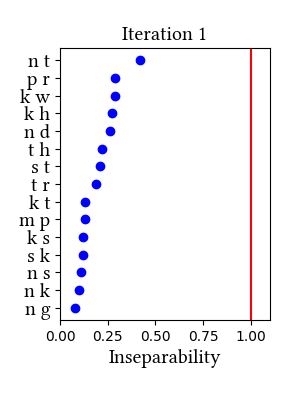
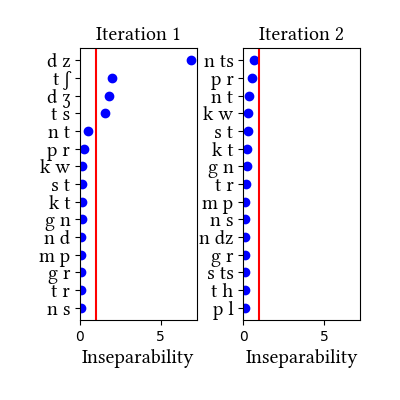
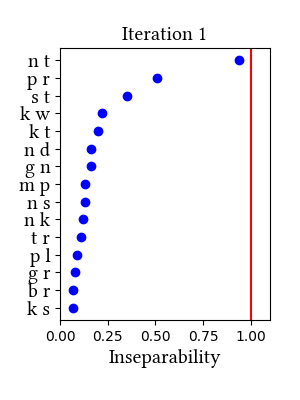
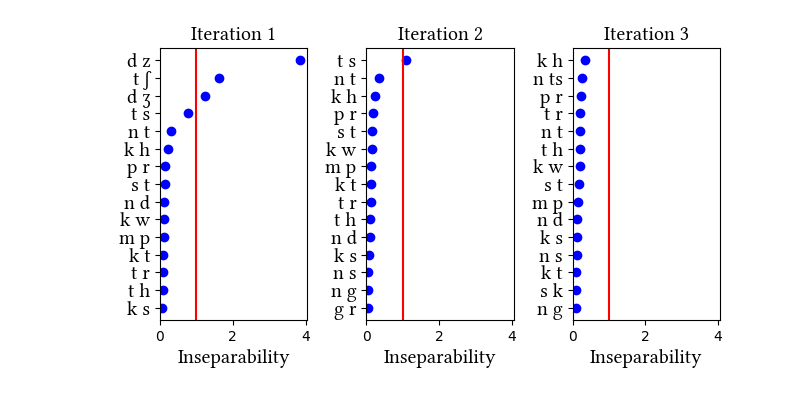
Latin has its own section in the paper, which reviews the arguments for [kw] and [gw] as complex segments. We find these arguments to be dubious. The "Affricated" version of the Latin dataset was created to test the hypothesis that complex segments have the distributions of singleton consonants because they come from singletons affected by systematic sound change. This simulation applies palatalization sound changes to Latin to create "pseudo-Italian" (Vulgar Latin, really).
Simulation data at a glance
Click on simulation name to view additional simulation details.
| Simulation name | Initial state Learning Data | Initial state features |
|---|---|---|
| Lewis-Short Affricated | LearningData.txt | Features.txt |
| Lewis-Short Classical | LearningData.txt | Features.txt |
| Paradigms Affricated | LearningData.txt | Features.txt |
| Paradigms Classical | LearningData.txt | Features.txt |
| Whitaker Affricated | LearningData.txt | Features.txt |
| Whitaker Classical | LearningData.txt | Features.txt |
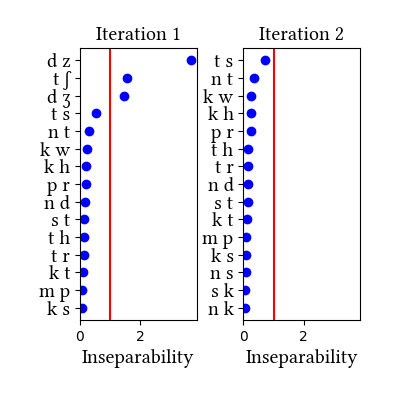
Simulation details for Latin lewis-short affricated
| Iteration | Learning Data produced | Features produced | Inseparability | New Segments added | Segments removed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
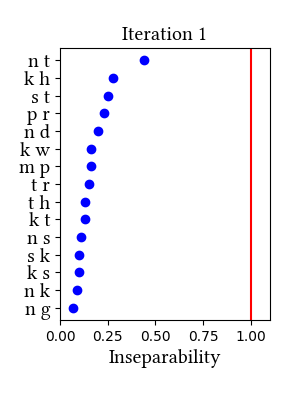
| 1 | LearningData.txt | Features.txt | [download] [view] | tʃ, dz, dʒ | ʃ, ʒ |
| 2 | No new learning data | No new features | [download] [view] | None | None |